We have previously mentioned PLC control panels in other posts on our blog. Chances are that, if you work in an industrial or manufacturing environment, you have at least heard of them. But what exactly is a PLC control panel and how does it work?
Originating in the 1960s, programmable logic controllers (or PLCs) are now ubiquitous across numerous industries. In this article, we will take a closer look at what they are and how they are used.
What Is a PLC Control Panel?
A PLC is an industrial modular device that can be programmed to perform many kinds of automated tasks. PLCs are often used in manufacturing environments—for example, to control the conveyor belts in a factory for the automotive industry. Another common application is controlling the rides in an amusement park. In the case of MAC Products PLC control panels, they are mainly used in the electric utility and electrified transit industries.
The Parts of a Control Panel
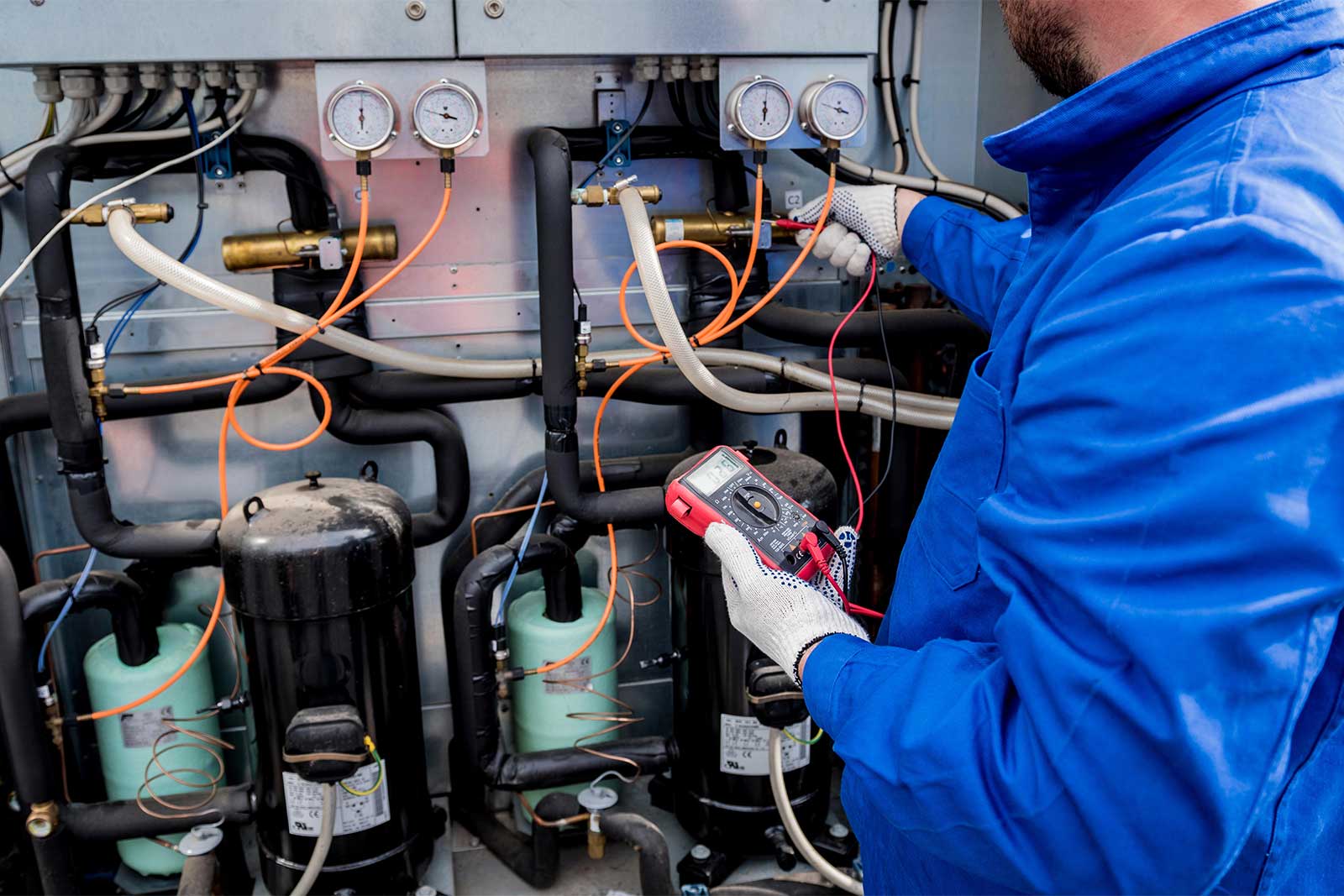
At its core, a control panel is simply a metal box that contains all the electrical devices that are used to manage a mechanical process. Inside the box, there is an enclosure, a back panel, wiring, a main breaker, various voltages, transformers, AC to DC power supplies, and more. A PLC Control panel consists of a rack with a CPU. This “brain” is the programmable part that performs the logic tasks according to the parameters you set.
One very important part of a PLC Control panel is the human-machine interface, or HMI. This vital tool enables the operator to interact with the PLC, access its data, and send data to it. This typically takes the form of a touch-screen interface. We are tremendously proud of the superior user-friendliness of the screens on our MAC PLC Control panels.
Programming a PLC
The PLC contains various input and output modules, depending upon the application for which the PLC is being used. For example, an input module might be responsible for managing a series of push buttons, alarms, or selector switches. Similarly, analog input modules are available to monitor a variable signal such as that which would be emitted by a pressure or temperature transmitter.
An output module might, for example, turn on a pump or a light. You program the PLC’s output to respond to various input factors. Communication modules for remote monitoring and control or dedicated device-specific modules (motion control) are other examples of potential ways to use a PLC.
Together, these input and output modules create a fully automated system.
Are There Different Types of PLC Control Panels?
As we have established, PLC control panels are highly versatile and can be used in many different ways. There are many different manufacturers of PLCs, all of which have their own slightly different way of doing things—for example, each manufacturer will have its own software system and cabling methods.
However, all PLCs consist of the same basic architecture and function in much the same way once set up and installed. The application of the PLCs varies much more than the setup and structure of the units themselves.
Here at MAC, for example, we manufacture PLC control panels that are used for critical infrastructure systems. This means that we have built extensive electromechanical redundancies into our PLCs. Should the PLC fail, an electrical circuit takes over in a manual mode. A PLC used for a less essential purpose—for example, to operate a conveyor belt in a factory—would likely be simpler and have fewer redundancies built in.
What Types of Systems Benefit From the Use of a PLC Control Panel?
PLCs, as we have seen, are tremendously versatile and used in many different applications. In this section, we will look at two essential areas of modern life that rely on PLC Control panels: power utility and electrified transit.
Power Utility
Reliable sources of power are essential to virtually all aspects of modern society, from the ways that we heat our homes and cook our food to the ways that we travel. This means that power utilities must be absolutely stable, with backups and redundancies in case of an emergency. (You can learn more about preparing power grids for emergencies in our recent article, “How to Prepare Your Power Utility for a Power Grid Emergency.”)
Before the advent of PLCs, these utilities were controlled by extensive and complex electromechanical control panels. PLCs have replaced these older control systems and simplified things tremendously as well as increasing flexibility.
Our PLC Control panels are used for pumping plant control systems. They allow for quick changes to be made (for example, to implement time delays) and for end users to connect into the system and monitor its conditions remotely. This enables faster and more informed responses in the event that any part of the system malfunctions.
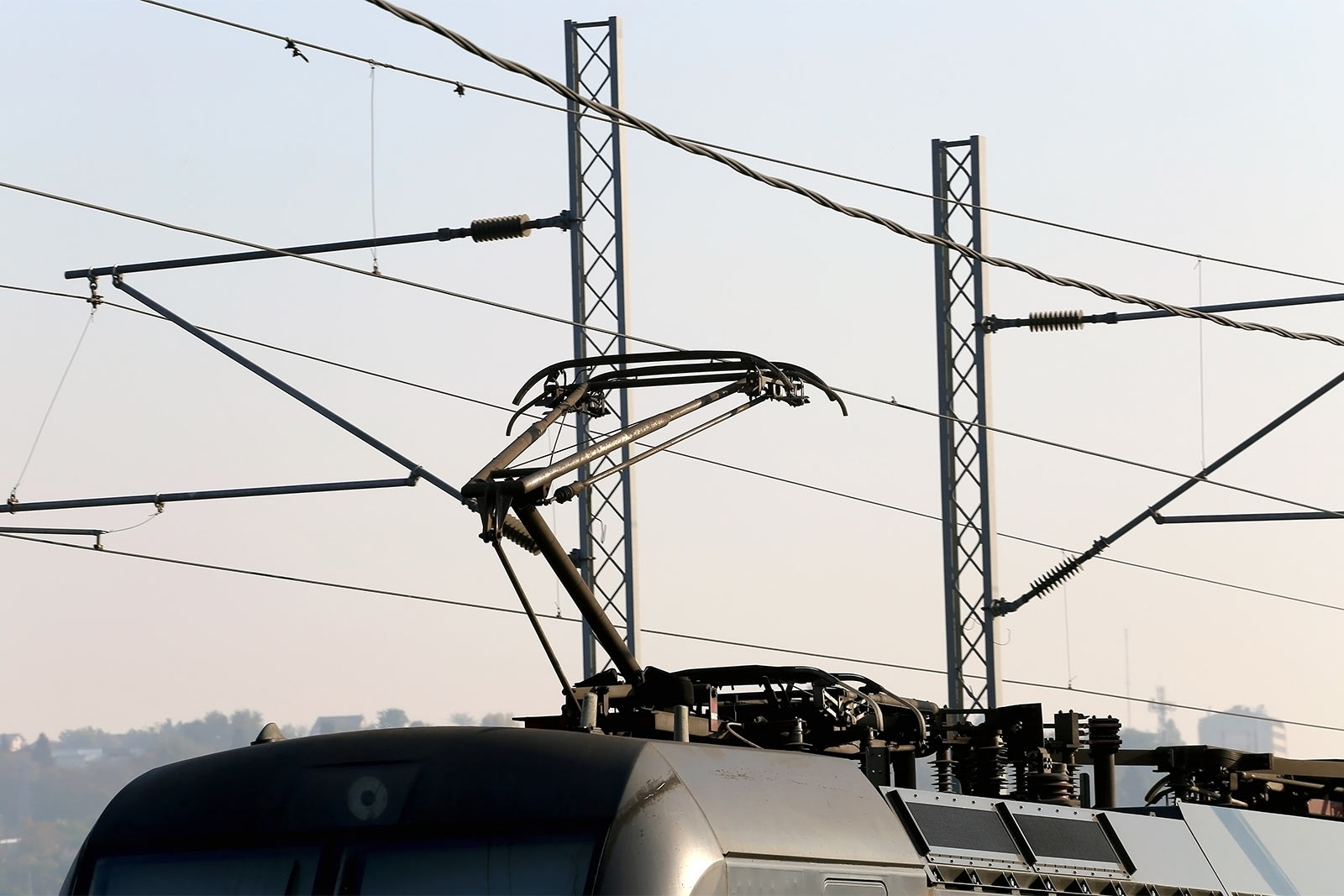
Electrified Transit
Electrified transit is becoming increasingly ubiquitous in towns and cities around the world as a sustainable and planet-friendly alternative to fossil fuel-powered transit. PLCs are commonly used in electrified transit systems—for example, to monitor and open or close switches and to control how the third rail in an underground train system is electrified.
As with the power utility application, the biggest benefits of using PLCs in the electrified transit industry are the ability to make swift automation changes, remote monitoring, and remote control. For example, engineers can wirelessly examine a certain signal, control a certain device, or network systems together.
Learn More
If you would like to learn more about MAC’s PLC Control panels or anything else we have discussed in this article, please contact MAC Products today. A member of our experienced team will be pleased to advise you.